SITEMAP
-
Baby Plan
-
PlanPregnancy
-
Delivery
-
Child Care
-
Global mam
-
Childcare Information
Let me brief you on uterine fibroid. Nothing is clear about the cause of uterine fibroid when there is no hormonal disorder. The most common cause of abnormal uterine bleeding in women of childbearing age is uterine fibroid. It is also the most common symptom that some doctors would willingly ignore even if it is what makes natural pregnancy hard to achieve. This is because it is too common a disease in women and many think that it doesn’t affect pregnancy. However, you cannot ignore uterine fibroid when it comes to natural pregnancy. Accurate diagnosis is critically important. Let’s move on to more details about it.
Uterine fibroid is a benign tumor generated from the smooth muscle comprising the muscle layers of the uterus. About 25% of all women experience this. Fibroids often vary in size from the size of granules to those with a diameter of 10 cm or larger, but there are no detectable symptoms. Uterine fibroid is divided into extramural fibroids located on the surface of the uterus, submucosal fibroids detected in the muscle beneath the endometrium of the uterus, and subserosal fibroids found underneath the mucosal surface of the uterus.
One of the most common symptoms is an increase in menstrual blood. This is attributed to the mucosal surface of the uterus which becomes widened by bigger fibroids. Generally, the uterine muscles contract to gradually decrease menstrual blood at the end of the period, but the uterine fibroids prevent the smooth muscle layer from making contractions properly to stop menstrual blood.Therefore, it won’t stop or increase in amount even when the period comes to an end.
Most of the fibroids are benign, but if they grow too fast, it can turn into a cancer called a sarcoma. A sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that occurs on the uterine wall. It is very rare, but be sure to have your health examined by a doctor or have ultrasonography performed on a regular basis.
Doctors typically diagnose a fibrous tumor through pelvic examination or ultrasonography. Fibrous tumors can be a determinant factor in your pregnancy planning depending on their size and location. The severity of the symptoms, a patient’s plan to get pregnant and the speed of fibrous tumor’s growth should all be considered based on each individual when treating it. If there is no symptom, you have no plan for pregnancy and the fibrous tumors do not press other organs, a simple observation may follow without any further treatment. But if you don’t have any special symptoms in your body caused by the fibroids but it has been difficult to get pregnant, a more objective and precise evaluation is needed.
Even if you have uterine fibroids, it is rare that they have a direct relation with the cause of infertility. Still, they must be examined at three-month intervals for their locations and sizes through ultrasonography before pregnancy.
Uterine fibroids can affect the process of fertilization and pregnancy depending on their location and size. If they’re extramural fibroids growing outside the wall of the uterus, they rarely affect the fertilization process. If they’re the submucosal fibroids in the muscle beneath the endometrium of the uterus, they may affect the process of pregnancy depending on their size and location. Nevertheless, it is rare even for a bigger fibroid to affect fertilization.
However, if they‘re the subserosal fibroids found underneath the mucosal surface of the uterus, particularly those that are like lumps within the uterine cavity, issues may be experienced in attempting to get pregnant. Even if pregnancy does occur, you will be prone to miscarriage.
Although the uterine fibroids are not critical factors in fertilization and pregnancy, they must be observed on a regular basis. If you’re planning for pregnancy, accurate and regular observation is required as those growing inside the uterine cavity can cause infertility, miscarriage or premature death when pregnant. Treatment is required through hysteroscopy. The medical equipment for the symptoms has been greatly advanced and it can be treated in a simple manner without you having to be hospitalized.
Internal medicine doctors easily discover legions in the stomach through gastroscope and we’re in the day and age when obstetricians can diagnose uterine disorders through hysteroscopy. Women who desire natural pregnancy should include hysteroscopy in the list of health checkups. Hysteroscopy can also discover any legions with polyp and perform treatment.
It can vary according to their locations and the methods used to remove them. If laparotomy or laparoscope was performed over the extramural fibroids or submucosal fibroids, you will want to try to get pregnant within 6 months. Still, you need to consult your doctor on the most appropriate period for you to get pregnant in because he or she is the one who is well aware of many facts observed through surgical operations. If big fibroids were operated on and the surface and the mucosal surface of the uterus have been penetrated, you must closely follow the symptoms even if you are pregnant and note that the C-section may be needed.
There indeed is a non-surgical method to remove fibroids. They are injections that prevent menopause temporarily, contracting the fibroids. Injections are needed every month for at least 3 to 6 months. A recently developed method is to find and block the blood vessels providing nutrients to the fibroids so as to make them small, this method is called transarterial embolization.
Note that these non-surgical methods are temporary ones. After the treatment is done, the fibroids often grow back in size. More studies are still under way regarding the risk of these methods before pregnancy, issues with reproductive ability, problems after pregnancy and the chances of recurrence.
A normal uterus is tilted forward. But a retroverted uterus is tilted backward instead. When there are fibroids in the anterior wall of the uterus, it can be tipped backward with the anterior end slightly convex. In effect, one out of five women has a retroverted uterus. Some women believe that it induces infertility as it makes it hard for sperms to swim through, but it is neither the cause of infertility nor a requirement of an operation.
But some reports say the frequency of miscarriage and bleeding during pregnancy may increase in women who have a retroverted uterus.
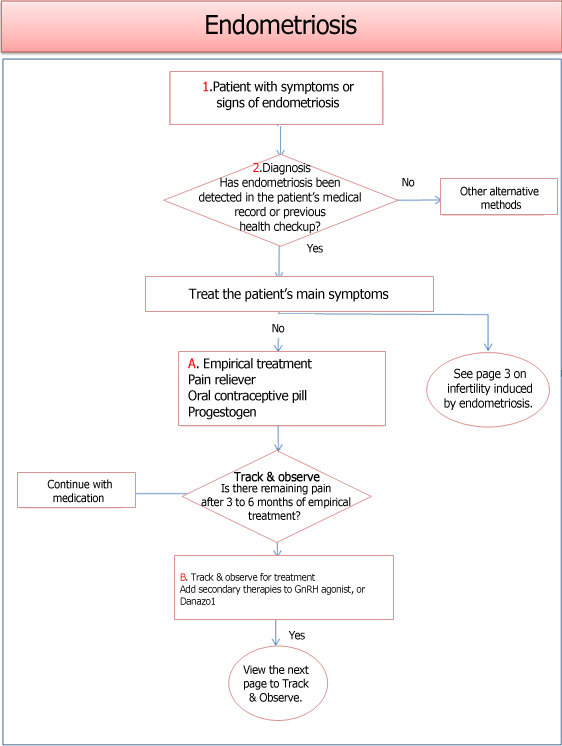
Endometriosis is a medical condition in which the cells on the lining of the uterus (endometrium) flourish outside the uterine cavity. About 7% of the women in their reproductive years suffer from infertility and pelvic pains due to endometriosis. No clear cause of endometriosis has been found, but some argue that the menstrual blood that retrogrades through the oviduct is the cause. Some scientists also argue it may be a symptom induced by the formation of blood vessels. This is because the blood vessels are more actively formed in the endometrium of females who have this symptom than those who don’t. If some of the endometrium is attached to the organs inside the abdominal cavity such as the bladder, intestines or ovary, it can flourish or shrink according to hormonal changes in menstrual periods alongside multiple other symptoms.
Even if you suffer from endometriosis, many females don’t experience any specific symptoms from it. They thus get pregnant without recognizing that they have endometriosis. But some studies report that a third of women suffering pelvic pains experience infertility.
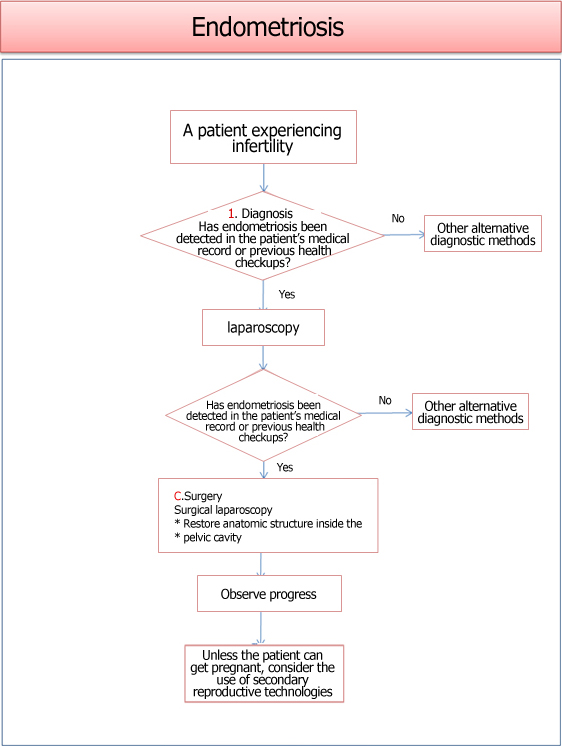
Endometriosis induces pelvic adhesions to stenosis, inevitably damaging the ovary or oviduct. If there is tubal endometriosis, tubal blockage can be an issue. When the tube is blocked, pregnancy is far from possible. In the event of ovarian endometriosis, the entire process of ovulation is shaken to the root. Endometriosis is the biggest and the most serious barrier to natural pregnancy because they mostly appear in the oviduct and ovaries, which makes it strongly associated with infertility.
The hereditary factor hasn’t been clarified yet, but a woman who has endometriosis often has a mother who had it in the past. Of course, her mother succeeded in bearing a child, which means it wasn’t severe enough to induce infertility. Still, if you as a mother have menstrual pain or sexual pain, you should closely check your daughter’s menstrual cycle and pain when she hits puberty. It is so true that early diagnosis leads to a better result.
Endometriosis is highly hereditary and is one of the most common causes of infertility in women. Therefore, mothers who experienced endometriosis must have your daughter examined by a gynecologist before marriage or pregnancy.
There are multiple classifications of endometriosis, but the most widely used system is the classifications set by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. It is divided into four stages of minimal, mild, moderate and severe depending on the degree of proliferation of endometriosis inside the abdominal cavity, related scars and level of adhesion.
The main symptom is menstrual pain with increased menstrual blood and possibly lengthened period. Other symptoms include pelvic pain and sexual pain. But some patients with a severe case of endometriosis don't experience specific symptoms. Doctors use selective treatment according to the severity of each case. There are several ways to adopt such as surgery or medication.
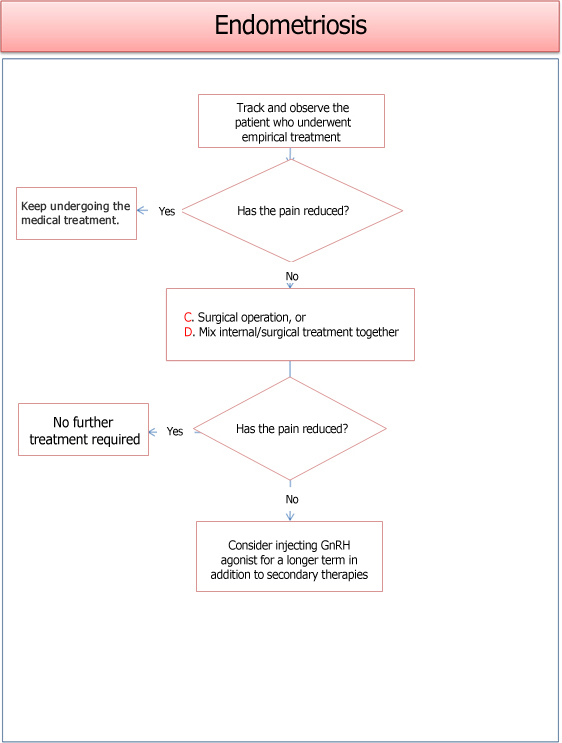
For a moderate case of endometriosis, medication is the first option to consider. Oral contraceptive pill can be taken or gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) analogues are injected once a month for 3 to 6 months to induce temporary menopause. Attempts for pregnancy is refrained during this period.
When it becomes clear that endometriosis is the cause of infertility, surgery will be performed immediately. Laparoscopy is mainly used to remove the endometriosis firsthand through laser or electric cauterization, or flapping is performed over the adhered area. If the result is positive, the patient can get pregnant within several weeks to months after the surgery.
Healthy life habits including a healthy regimen and exercise are helpful for alleviating the symptoms of endometriosis. It is not scientifically proven that disciplining your body and mind is helpful but it is known to be helpful for patients with endometriosis. In particular, yoga increases blood circulation around the pelvis and provides fresh oxygen to legions, which can do some good in preventing and treating the symptoms. Always remember that regular exercise is good for you, while too much of it can disrupt your immune system.
Women with endometriosis are susceptible to abdominal discomfort when they fail to take carbohydrates of diverse types, so they must eat balanced meals for a comfortable stomach. Taking supplementary nutrients such as omega-3 fat, vitamin A, C and E, minerals like selenium and zinc is a very good way to alleviate your symptoms. Some say herbal tea with no caffeine also helps, so try to drink less coffee and get used to herbal teas. When you do this, get some expert advice to find out which teas are safe to drink.
If the patient fails to respond to medication but surgery is not an option, assisted reproductive technologies such as ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination (IUI), or in vitro fertilization (IVF) can be helpful to get pregnant. Endometriosis is recurrent as long as you have the ovary. Therefore, use any proven methods available to get pregnant.
[ Source: Kims Online (kimsonline.co.kr) ]
[ Source: Kims Online (kimsonline.co.kr) ]
[ Source: Kims Online (kimsonline.co.kr) ]
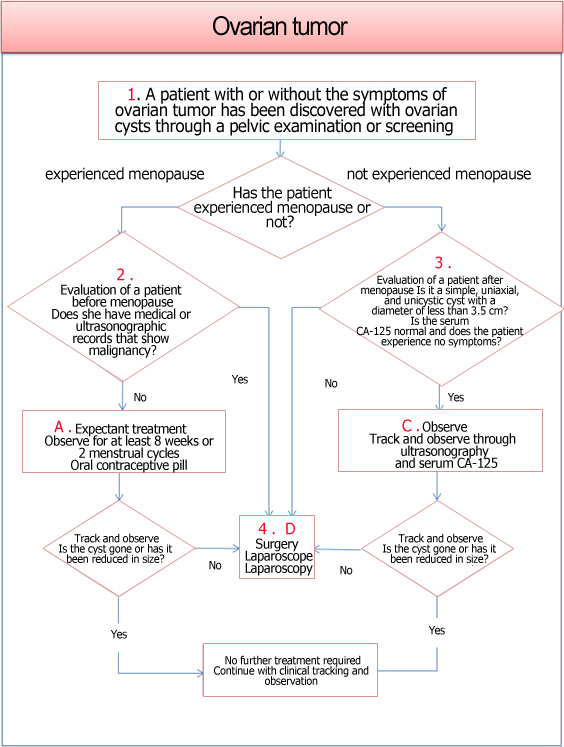
Having a tumor (lump) in your ovary does not mean you have cancer. Tumors are one of the most common diseases to appear in the ovaries and most of them are benign. Cystoma refers to a benign tumor in the ovary. About 80% to 85% of the ovarian tumors that appear in women in their reproductive period are benign. They may have a solid form or a cyst form filled with fluids. Still, you have to have an expert examine them through ultrasonography to see if they have the potential to turn malignant. If the tumor is over 8 cm in size, contains solid content, a tunica media inside the cystoma, or it is small but you experience negative symptoms, they should be surgically removed. If cystoma won’t reduce in size even after a few months, it should be surgically removed.
Sources from B through D: Prof. Jeongyeol Han (Obstetrics and Gynecology, Cheil General Hospital of Kwandong School of Medicine)
Chief Director of Korea Mother Safe Counseling Center